MODULE 1. Interprofessional working in early detection of breast cancer
5. Oncogenetic consultation
Oncogenetic counselling
Oncogenetic counselling is offered to any type of patients diagnosed with cancer. Its goal is firstly, to create a family tree focused on the family history of tumours; secondly, to propose the search for genetic mutations according to the oncological risk. If a hereditary predisposition is detected in the patient, a targeted genetic test, in search of the detected mutation, is offered to family members who wish it. Different professionals are involved in these consultations: genetics physician, genetics counsellor (a new profession recognized only in some countries and/or states) and a psychologist.
The criteria for genetic analysis have a common basis. Depending on the country and its health system, they vary but mainly take into account
During this first interview, the genetic counsellors inform the patient about the proposed analysis, the plausible results as well as the modes of transmission, the medical and psychological implications and finally the possible risk incurred by the other members of the family.
Psychological support is advisable and should be available at any time during the process. This support may take different forms: individual counselling as well as support groups. The possibilities to educate genetic counsellors at a master level exist in Europe, yet available in France and the United Kingdom. Generally, a substantial part of their training focuses on the importance of psychology aspects. Hence, according to Samson and al (2014), once the results received, patients often express different negative feelings such as: sadness, anger, fear or anxiety, leading to increased patient vulnerability and powerlessness. These are the main reasons why support from competent health care workers and peers is essential.
The criteria for genetic analysis have a common basis. Depending on the country and its health system, they vary but mainly take into account
- Age of breast cancer onset even without family history
- Number of members with breast cancer, regardless of the age of onset or not
- History of bilateral breast cancer and the age of onset of the primary cancer
- Breast and ovarian cancer in the same person, regardless of the age of onset or not
- Several family members with ovarian cancer
- Male breast cancer, regardless of the age of onset
- Family origins
During this first interview, the genetic counsellors inform the patient about the proposed analysis, the plausible results as well as the modes of transmission, the medical and psychological implications and finally the possible risk incurred by the other members of the family.
Psychological support is advisable and should be available at any time during the process. This support may take different forms: individual counselling as well as support groups. The possibilities to educate genetic counsellors at a master level exist in Europe, yet available in France and the United Kingdom. Generally, a substantial part of their training focuses on the importance of psychology aspects. Hence, according to Samson and al (2014), once the results received, patients often express different negative feelings such as: sadness, anger, fear or anxiety, leading to increased patient vulnerability and powerlessness. These are the main reasons why support from competent health care workers and peers is essential.
References
- Samson, A., DiMillo, J., Thériault, A., Lowry, S., Corsini, L., Verma, S., & Tomiak, E. (2014). Living with the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic mutation: Learning how to adapt to a virtual chronic illness. Psychology, health & medicine, 19, 103-114 doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2013.779729
- Shiovitz, S., & Korde, L. A. (2015). Genetics of breast cancer: a topic in evolution. Annals of Oncology, 26, 1291-1299. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv022
Genetic basis and main genes involved in breast cancer
Introduction
Breast cancer is the leading cause of death among women, one in eight women will be affected during her lifetime. All of these cancers are not of hereditary kind. Between 65% and 80% are cancers of sporadic appearance, 15-25% are of familial nature and about 5-10% are linked to hereditary predispositions. Among all predisposition genes, we will focus on the more frequently involved ones, namely genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. These two genes are present in every human being, regardless of sex.
Gene function
BRCA1 and BRCA2 are genes that have a protective role against tumours. Indeed, BRCA1 has an important role in repairing the damage to the RNA as well as in transcript regulation. As for BRCA2, its role is to maintain genome stability, by repairing DNA.
Mutations, associated cancers and risks
These are genes that are part of the tumour suppressor class with a role in repairing DNA damage.
A change in the sequence induces instability in the repair process and can lead to the formation of a tumour. A mutation in these genes exposes us to a higher risk of cancer, mainly breast, ovarian and fallopian tube cancer. Generally speaking, breast cancer associated with BRCA 1 and 2 occurs earlier on average than sporadic breast cancers. Mutations in BRCA 2 increase the risk of prostate and breast cancer among males. |
Genetic risk factors and evolution
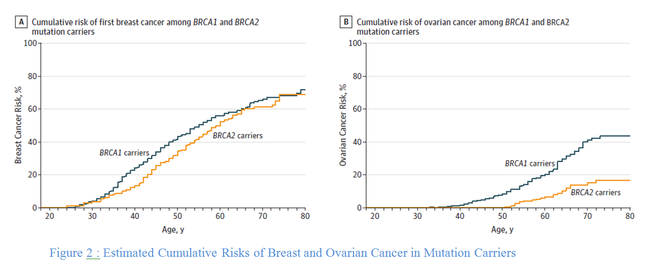
The basic risk for a woman of the general population with no particular family history of developing breast cancer in her lifetime is 12%. With the presence of a mutation on BRCA 1 and 2, the lifetime risk of developing breast cancer increases to 70%. Moreover, someone who had been diagnosed for a first breast cancer and who has a BRCA 1 or 2 mutation has an increased risk of contralateral breast cancer. These results justify the implementation of the specific monitoring or management measures discussed in this chapter.
References
- World Cancer Research Fund International (n.d.), Breast cancer statistics. Repéré à https://www.wcrf.org/int/cancer-facts-figures/data-specific-cancers/breast-cancer-statistics
- Kuchenbaecker KB, Hopper JL, Barnes DR, et al. Risks of Breast, Ovarian, and Contralateral Breast Cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers. JAMA. 2017;317(23):2402–2416. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.7112
- Powell, S., Kachnic, L. (2003), role of BRCA1 et BRCA2 in homologous recombination, DNA replication fidelity and the cellular response to ionizing radiation. Oncogene. Vol. 22, 5784-5791
- Shiovitz, S., Korde, L. A., (2015), Genetics of breast cancer : a topic in evolution, Annals of Oncology, vol. 26, 1291-1299
Images
- Opensource images at UTL :
https://www.genome.gov/glossary/resources/karyotype.pdf - Kuchenbaecker KB, Hopper JL, Barnes DR, et al. Risks of Breast, Ovarian, and Contralateral Breast Cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers. JAMA. 2017;317(23):2402–2416. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.7112